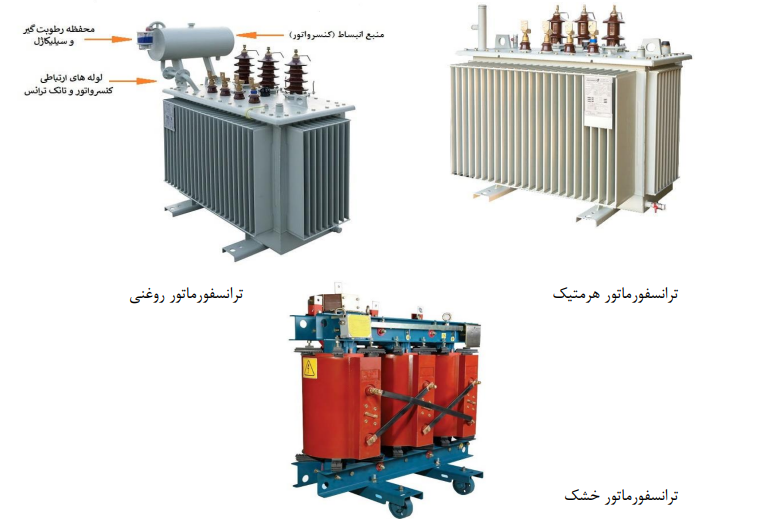
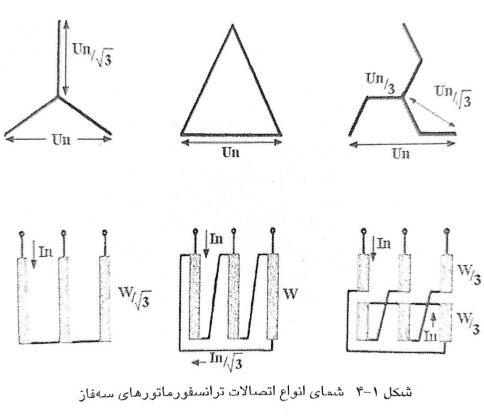
General description of the transformer
When there is mutual induction between two coils, any change in the current will induce a voltage in the other coil, this principle is used in transformers. Each transformer has a primary coil and a secondary coil, the primary coil takes energy from the source and transfers it to the secondary coil through changing the magnetic field. Energy appears as a driving force in the secondary.
Using transformers, electrical energy can be transferred from one circuit to another circuit, without establishing an electrical connection between them, this complete energy transfer is carried out by the said magnetic field. Transformers play a unique role in the distribution of AC electric power because they can convert electric power with a certain current and voltage into power with the same value but with a different voltage and current level.
Applications and advantages of three-phase transformer
Three-phase transformers are one of the most important means of energy transmission that make up large parts of electrical networks. These transformers are produced by some companies that manufacture electrical equipment
they become
The main purpose of using three-phase transformers is to transfer, transform (decrease or increase) electrical energy. As you know, the main power of an electrical network is produced in a certain range. Three-phase transformers in this sense transfer energy from an electrical network to so these transformers act as an important energy transmission system. Also, one of the main strengths of using three-phase transformers is that these transformers are used as an energy distribution system. take
Transformer maintenance
Transformer damage usually happens in two ways:
- Disconnection of transformer conductors (burning of weak and strong pressure coils)
- Conduction of the transformer insulation (loss or loss of properties of a part of the insulation)
The most common attention given to transformers is the appearance evaluation, in general, the appearance evaluation generally includes checking the external conditions and the cooling system. Transformers should be checked and evaluated periodically so that problems can be detected and corrected in the early stages, before major repairs are needed.
Inspection of transformers for maintenance is usually done once a week as a routine, however, the frequency of visits can be different. For example, if there is an indication that there is a problem that is spreading, the frequency of visits can be increased. The maintenance period of the transformer should be determined based on the reliability requirements of the equipment and the instructions recommended by the manufacturer.

Maintenance activities may be performed for any category of facilities in time intervals, but most industries usually perform a general shutdown once or twice a year for maintenance purposes. In the following, the usual activities for each of the transformer maintenance actions are examined.
Routine inspections and minimal transformer repairs
- Check connections and equipment connected to it
- Check oil level and cooling system
- Fasteners and control systems
- Visual inspection and leakage
- Measurement of insulation resistance values
- Analysis of gases from the Buchholz relay (oil sampling)
- Reconnection or replacement of silica gel in the breathing chamber
- Check ground connection
Routine repairs
- Opening the trans to inspect and circulate the oil or replace it
- Checking and testing bushings
- Repair of transformer components including conservator, tank, cooling system, sealing washers
Major repairs and overhauls
- Pressing core sheets
- Replacement of coil connections and bushings
- Active part overhaul
- Opening the transformer to replace the windings and insulation
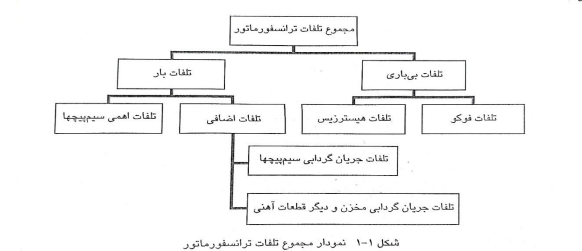
Common causes of transformer damage
overload
If the overvoltage of the network causes the voltage of the conductors to increase with respect to the body or with respect to the other phase to a value greater than the insulation endurance or dielectric endurance, an electric arc occurs in the insulation and the insulation loses its properties. In the continuation of this process, if the high voltage is established continuously, the leakage current of the insulation will gradually increase and the temperature of the insulation will rise and eventually it will be damaged. Of course, in this situation, the protection switches of the transformer must be activated. If the load of the transformer increases, due to heat generation in the transformer, it causes the conductors to break in the weak points of the transformer, which mostly happens in transformer motors with zigzag windings at the connection point. To prevent damage caused by external transient overvoltages such as lightning, the most appropriate way is to install a lightning arrester.
Mechanical damage
As a result of factors such as incorrect transportation of the transformer with a crane or any other device, due to strong shocks, the core of the transformer which is fixed on the body is moved and causes the connection of the conductors to break. Also, if a short circuit occurs at the input or output of the transformer, the conductors of the transformer exert a lot of force on each other due to the connection. These forces may cause rupture of the conductors or damage to the dry insulation of the transformer, or damage to the transformer body.
rise in temperature
An increase in the internal temperature of the transformer to a greater extent than the insulation tolerance of the transformer will damage it. If the temperature rises, the conductivity of the insulators increases, unlike the conductors, and excessive leakage current in the insulation causes the transformer to burn. One of the reasons for the increase in the temperature of the transformer is the increase in the ambient temperature. The temperature of the working conditions to receive the rated power is determined by the manufacturer. Also, the amount of power reduction due to temperature increase should also be stated by the manufacturer. To solve this problem, a cooling system with higher efficiency can be used.
Transformer aging
When the transformer is used for a long time in the network, the dry insulation of the transformer gradually loses its original properties, which does not return to its original state even after changing the oil. The useful life of the transformer is usually announced by the manufacturer. Using accessories such as high-quality transformer oil and suitable gaskets for sealing is very effective in increasing the life of the transformer.
Problem with transformer oil
If the oil level inside the transformer decreases and instead air penetrates inside the transformer tank, due to the low electrical resistance of air compared to oil, an electric arc occurs. Frequent visits to the transformer can be helpful in this regard. The height of the oil in the oil glass, wetness on the cap, radiators and under the transformer is a good measure of knowing the oil leak.
Moisture penetration
The presence of water particles in the oil greatly reduces the electrical resistance of the transformer oil, which causes arcing in the transformer oil. Sampling and testing the oil of transformers in predetermined periods provides accurate information on the penetration of moisture into the transformer tank.
Pollution of transformer oil
During the working period of the transformer, due to the circulation of oil between the conductors and the core, the oil gets old and particles are separated from their surface, and these particles are accumulated in the form of sludge and deposits at the bottom of the tank and on the active part of the transformer. In addition, the presence of particles in the oil reduces the electrical resistance of the oil. Scheduled oil testing is a good way to find out the presence of transformer oil contamination.
Transformer oil causes heat transfer and insulation of electricity. Between the windings, between the sheets and around the core and internal connections, it acts as an insulator and prevents short circuit. At very high voltages, there is a possibility of short circuit due to current jump, which the oil prevents this by protecting it. Sometimes the core of the transformer heats up strongly during the formation of the magnetic field in different parts and causes the winding to melt and as a result the transformer fails. For this reason, the body of the transformer is made in the form of fins so that the heat can be transferred to the open air more quickly.
It is necessary to mention that the oils used in transformers are produced in two types, one and two, and type one is used in distribution transformers.
Transformer repairs
In general, in the repair of industrial transformers, the following items are replaced or repaired:
- Catching transformer oil leaks
- Replacing or repairing the voltage adjustment tap changer switch
- Replacing or repairing the transformer core
- Repair or replacement of transformer parts and equipment (bushes, shoes, wooden parts, etc.)
- Repair and rewind low-voltage bobbins or replace low- and high-voltage bobbins
- Replacing or repairing defective transformer peripheral equipment
Effective parts in the failure of transformers
Coils
Coils fail when their insulation is lost. The insulation of the coils may be destroyed due to moisture, temperature rise, vibration, overuse of transformer power and mechanical pressure resulting from breakdowns.
bushing
Bushings are damaged due to arching, wear and increasing life and passage of time. Also, internal pollution and humidity prevent the bushings from working properly. You should also note that the failure process of bushings is not easy to detect.
core
The damage that occurs to the core occurs in the case of core separation or an increase in the temperature of the core due to short-circuiting.
Destruction of insulation
Deterioration of the insulation leads to an increase in the short circuit in the magnetic flux to produce a stable short circuit current and these connections produce excessive heat which may cause many problems.
مشکلات دیگر
There are other reasons that cause transformer failure, such as: oil contamination, oil leakage, abnormal voltage, and natural events such as lightning, flood, fire, etc.
What factors cause failure of coils?
- Instability of insulation on conductors
- The presence of a short circuit between adjacent rings
- Short circuit due to moisture
- Loss of insulation around the side of the transformer due to improper drying operation when voltage is applied
- Transient waves can cause a short circuit and eventually lead to a hole in the insulators.
Transformer troubleshooting and repair training
Transformer troubleshooting is done in the following two ways:
- Gas analysis
- periodic tests
In the transformer troubleshooting method by gas analysis method, oil sampling is done as usual. After that, the gas is separated from the oil and the gas analysis is done, and the problems of the transformer can be determined based on the percentage of gases in the oil. According to the ratio of gases, it is possible to detect phenomena such as partial discharge, corona discharge, arc with high temperature and overload in the transformer and identify the defect inside the transformer.
The insulating oil of the transformer must have the ability to absorb gases under pressure so that by analyzing the gases dissolved in it, it is possible to identify the failure and the causes of abnormal conditions in the work of the transformer. Hydrogen compounds along with simpler hydrocarbons such as methane, ethane, ethylene and acetylene create different ratios which can be checked as an indicator of the temperature produced in the transformer oil. For example, a high amount of hydrogen indicates ion bombardment due to partial discharge.
Based on IEEE standard table, we can identify these disadvantages more correctly.
| Evaluation levels | Conditions | TCDG value |
|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | If the gas level in the oil is at this level, it indicates that the trans is healthy. | 720 |
| Level 4 | If the amount of TCDG is at this level, it means that the flammable gas is more than the normal working condition, so it needs more inspection. It is possible that the transformer has several malfunctions. | 721-1921 |
| Level 7 | The presence of TCDG at this level indicates that the top level of the oil is breaking down. More inspection and handling should be done. It means there is one or more errors and we need to repair the transformer. | 1921-4620 |
| Level 9 | The value of TCDG at this level indicates a serious problem, and the transformer should be repaired as soon as possible, and the work may lead to failure. | >4620 |
Various tests are performed to repair the power transformer, which are discussed below.
1. Testing the windings:
Transformer windings are examined and tested from the following aspects:
- cut off
- Having a connection with other points of the transformer
- Damage or wear of the insulation system
- Change of physical location
- Loose connections
2. Measuring the ohmic resistance of transformer coils:
During the repair of the power transformer, any connection, damage, loosening and excessive wear of the coils will change their ohmic resistance, by measuring the ohmic resistance of the coils, it is possible to find out the existence of defects in the transformers.
3. Testing the conversion ratio of the coils:
The ratio of the voltage of the high pressure part of the transformer to the voltage of the low pressure part of the transformer is the conversion ratio of the transformer. By measuring this value in practice and comparing it with the nominal value of the ratio stated in the transformer plate, it is possible to understand the health of the transformer windings. When the conversion ratio is different from its nominal value, it means that a significant number of wire bobbins are out of line.
4. Transformer polarity test:
The polarity of the transformer is related to its internal connections. In the maintenance and repair of the transformer, it should be noted that the correct polarity of the transformer is important when several transformers are to be connected in parallel.
The polarity test of the transformer is done in two ways during the repair of the industrial power transformer.
- Using induction shock
- By applying alternating voltage
How to prevent transformer overload?
Optimum selection of transformer power is very important for feeding the network. Aswal considers the presence of load between 30 and 40% as low load and the presence of load more than 70% is called high load. They use the amperage method to check the overload of the transformer. In this way, it checks the transformers in terms of the number of blown fuses and the number of key drops in the previous day, and as a result of checking, if the transformer is overloaded, they replace the transformer with a higher power.
To prevent overloading of transformers, it is better to use standard connections at the ends of beams and electrical panels and fuse boxes.
Common maintenance and troubleshooting tests of transformers
In the following, we will examine the routine tests of the transformer components, which are performed for the purpose of maintenance and troubleshooting.
core
- Insulation resistance
- Ground test
insulating oil
- Dielectric strength test
- Power factor-loss factor
- Acid count
- Oxygen inhibitor
- Analysis of dissolved gases
Bushings
- Dielectric losses
- power factor
- oil level (if possible)
- Visual inspection for cracks and dirt
- temperature
Conservator
- Level gauge calibration
- appearance (oil leakage and diaphragm leakage)
- Intake air system
Store and accessories
- Wire temperature indicator
- Infrared temperature scan
- defect analysis (ultrasonic)
- Vibration analysis
- Buchholts relay (appearance and ohmic checking)
- Pressure fault detection relay (function test)
- Analysis of the hundred
Cooling system
- Pump bearings (vibration, sound and temperature)
- Check the radiator
- Fans and control (check rotation)
- Cleanliness of fan and radiator blades
- Oil pumps
Coils
- Leakage impedance-reactance voltage drop
- Excess current and resistive losses
- Frequency response analysis (SFRA)
- Power factor-loss factor
- DC resistance
- Conversion ratio
Attachments:

General description of the importance of transformer oil testing:
Paying attention to the fact that many power transformers in the world have a lifespan between 30 and 40 years, so the possibility of causing errors and being out of circuit increases. This will cause a lot of problems, including the withdrawal of the transformer from the network, which on the other hand will cause material damage and damage to the stability of the network or the stability of networks, so this issue is considered to be very important to measure the condition of the network, especially power transformers. .
In evaluating the condition and life measurement of transformers according to various oil and electrical tests, as well as with the analysis performed on the results of these tests, it is possible to obtain a real result of the condition of the transformer and compare it with its design life, and practically solutions for Optimum use of the transformer and as a result increase its lifespan.
Transformer oil prevents transformer destruction. Transformer oil is an insulating liquid and in addition to its insulating function, it also has the role of heat transfer in the transformer.
As a result of atmospheric conditions, the type of loading from the transformer and incidents that may affect the oil. Transformer oil deteriorates over time. This breakdown of the oil causes the oil to lose its insulating properties and so-called aging. The aging of the transformer oil over time causes serious problems and ultimately damages or imposes on the transformer.
Among all the testing techniques for transformer oil, gases dissolved in oil are the most important method. These gases are the result of oil degradation, which occur due to various conditions, such as breakdown or defect in the transformer. These gases are also an indicator of transformer destruction.
These gases can be analyzed separately using gas chromatography methods. More than 30 years have passed since the formulation of standards related to methods based on oil analysis such as gas chromatography and its implementation, these methods can only provide a general indicator of the condition of the transformer. Various tests are performed to diagnose and evaluate the condition of the transformer, including oil tests, including quality control and gas chromatography tests, filters, and electrical tests, including measuring the insulation resistance of the coils, measuring the insulation loss coefficient, measuring the resistance Ohm and conversion ratio, pointed out. There is another category of tests which are referred to as modern tests. These tests include partial discharge measurement (PD), polarization and polarization current measurement (PDC), and frequency response measurement (FRA).


